145 Degrees F To C
elan
Sep 15, 2025 · 6 min read
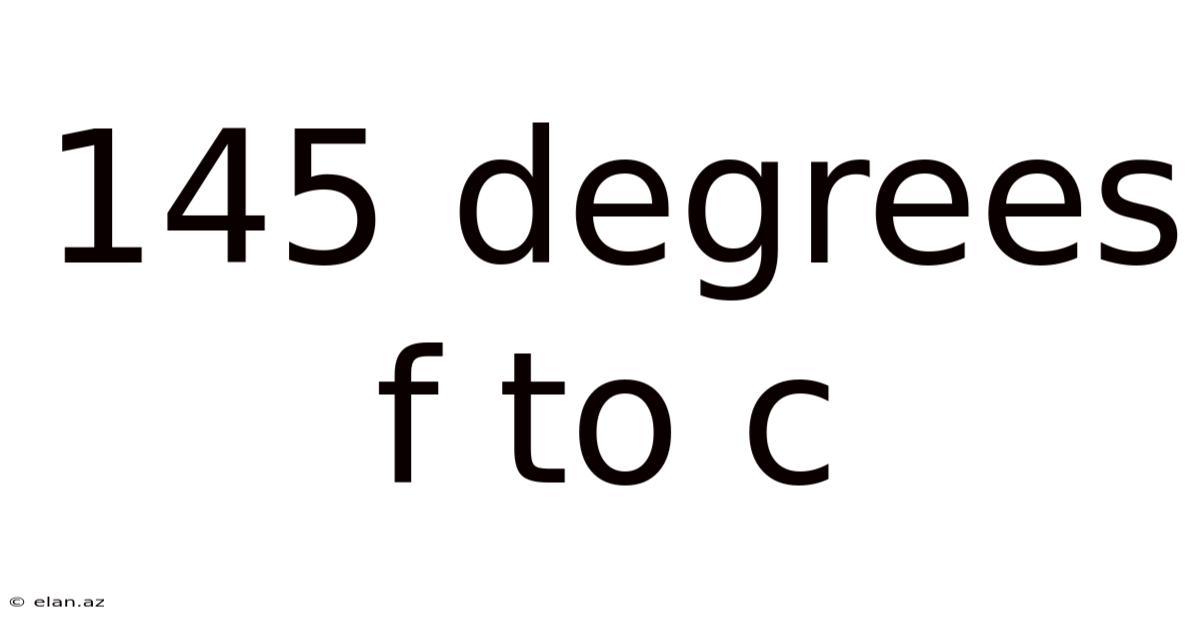
Table of Contents
145 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Converting temperatures between Fahrenheit (°F) and Celsius (°C) is a common task, particularly in cooking, scientific research, and everyday life. Understanding this conversion is crucial for ensuring accuracy and safety, especially when dealing with temperatures critical to food safety or industrial processes. This comprehensive guide will not only explain how to convert 145°F to °C but also delve into the underlying principles of temperature scales, provide practical applications, and address frequently asked questions. We’ll also explore the significance of 145°F in specific contexts.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius Scales
Before diving into the conversion, let's briefly review the two temperature scales. The Fahrenheit scale (°F), developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, is a scale where the freezing point of water is 32°F and the boiling point is 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure. The Celsius scale (°C), also known as the centigrade scale, was devised by Anders Celsius. In this system, the freezing point of water is 0°C and the boiling point is 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure. The key difference lies in the size of the degree intervals between these points.
Converting 145°F to Celsius: The Calculation
The conversion formula from Fahrenheit to Celsius is:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
Let's apply this formula to convert 145°F to Celsius:
°C = (145°F - 32) × 5/9
°C = 113 × 5/9
°C = 62.78°C (approximately)
Therefore, 145°F is approximately equal to 62.78°C.
Practical Applications of 145°F (62.78°C)
The temperature of 145°F (62.78°C) holds significant importance in several areas:
-
Food Safety: In many countries, 145°F (62.78°C) is the minimum internal temperature recommended by food safety agencies for cooking poultry, to ensure that harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Campylobacter are eliminated. Cooking poultry to this temperature is crucial for preventing foodborne illnesses. Using a meat thermometer is essential to guarantee the food reaches this temperature throughout. Failure to achieve this temperature can lead to serious health risks.
-
Pasteurization: This temperature plays a role in the pasteurization process for certain food products. Pasteurization, a heat treatment, eliminates or reduces the number of microorganisms that cause spoilage and disease. While the exact temperature and time vary depending on the product, 145°F (62.78°C) might be used in some pasteurization methods.
-
Industrial Processes: Many industrial processes, particularly in food manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, and chemical engineering, require precise temperature control. 145°F (62.78°C) might be a critical temperature threshold in various stages of production, ensuring the quality, safety, and efficiency of the process.
-
Scientific Experiments: In scientific experiments involving biological samples or chemical reactions, maintaining a precise temperature is paramount. 145°F (62.78°C) could be a target temperature in various experiments, depending on the nature of the research.
The Significance of Accurate Temperature Measurement
The accuracy of temperature measurements is crucial, especially in applications like food safety. Using inaccurate thermometers or misinterpreting temperature readings can have significant consequences. For example, undercooking poultry to below 145°F (62.78°C) can lead to bacterial contamination and foodborne illness. Similarly, overcooking can result in dry, less palatable food. Investing in a reliable thermometer and understanding how to use it properly is essential.
Beyond the Conversion: Understanding Temperature's Impact
Temperature significantly affects various properties of materials, including their physical state (solid, liquid, gas), chemical reactivity, and biological activity. For example, changes in temperature can cause substances to expand or contract, alter reaction rates, and affect the growth and survival of microorganisms. Understanding these effects is crucial in numerous fields.
Different Types of Thermometers
Accurate temperature measurement depends heavily on the type of thermometer used. Various thermometer types exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
-
Liquid-in-glass thermometers: These traditional thermometers utilize the expansion and contraction of a liquid (often mercury or alcohol) to indicate temperature. They are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, but they can be fragile and less precise than other types.
-
Digital thermometers: Digital thermometers use electronic sensors to measure temperature and display the reading digitally. They are often more precise, quicker to read, and more durable than liquid-in-glass thermometers. These are commonly used in food safety applications.
-
Thermocouples: These are sensors that measure temperature based on the voltage generated by two dissimilar metals when a temperature difference exists between them. They are highly accurate and can measure a wide range of temperatures, making them suitable for industrial applications.
-
Infrared thermometers (non-contact): These thermometers measure temperature by detecting infrared radiation emitted by an object. They are contactless and are useful for measuring the temperature of surfaces without physical contact.
Choosing the appropriate thermometer depends on the specific application and the required accuracy.
Factors Affecting Temperature Measurement
Several factors can influence the accuracy of temperature readings:
-
Calibration: Thermometers should be regularly calibrated to ensure accurate readings. Improper calibration can lead to significant errors.
-
Sensor Placement: The placement of the thermometer sensor is critical. For example, when measuring the internal temperature of food, the sensor should be placed in the thickest part of the food to ensure the most accurate reading.
-
Environmental Factors: Ambient temperature and humidity can affect the accuracy of some thermometer types.
-
Thermometer Response Time: Some thermometers have a faster response time than others, meaning they reach a stable reading quicker. This is important in applications where rapid temperature changes occur.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the difference between Fahrenheit and Celsius?
A: Fahrenheit and Celsius are two different scales for measuring temperature. Fahrenheit has a freezing point of water at 32°F and a boiling point at 212°F, while Celsius has a freezing point at 0°C and a boiling point at 100°C.
Q: Why is 145°F important in food safety?
A: 145°F (62.78°C) is the minimum internal temperature recommended for cooking poultry to kill harmful bacteria like Salmonella and Campylobacter, significantly reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
Q: Can I use a different formula to convert 145°F to Celsius?
A: While the formula (°F - 32) × 5/9 is the standard, there are other mathematically equivalent formulas that achieve the same result. However, the standard formula is generally preferred for its simplicity and clarity.
Q: How can I ensure accurate temperature measurements when cooking?
A: Use a calibrated, reliable food thermometer, insert it into the thickest part of the food, and wait until the reading stabilizes before removing it. Avoid touching the food with your fingers to check for doneness.
Q: What happens if I don't cook poultry to 145°F (62.78°C)?
A: Undercooked poultry can contain harmful bacteria that can cause food poisoning, leading to symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. In severe cases, it can lead to hospitalization.
Conclusion
Converting 145°F to Celsius (approximately 62.78°C) is a straightforward process using a simple formula. However, the significance of this temperature, particularly in food safety, extends beyond the mathematical conversion. Understanding the importance of accurate temperature measurement, utilizing appropriate tools, and following food safety guidelines are crucial for ensuring both food safety and the overall success of various applications where precise temperature control is necessary. Remember that diligent adherence to safe cooking temperatures significantly reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses and contributes to overall well-being. Always prioritize safety and accuracy when dealing with temperature measurements.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
150 Square Meters To Feet
Sep 15, 2025
-
Meaning Of Chaos In Urdu
Sep 15, 2025
-
Parametric Vs Non Parametric Statistics
Sep 15, 2025
-
Pictures Of Volcanoes To Draw
Sep 15, 2025
-
Bird Names Beginning With I
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 145 Degrees F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.