2 Methyl But 2 Ene
elan
Sep 18, 2025 · 7 min read
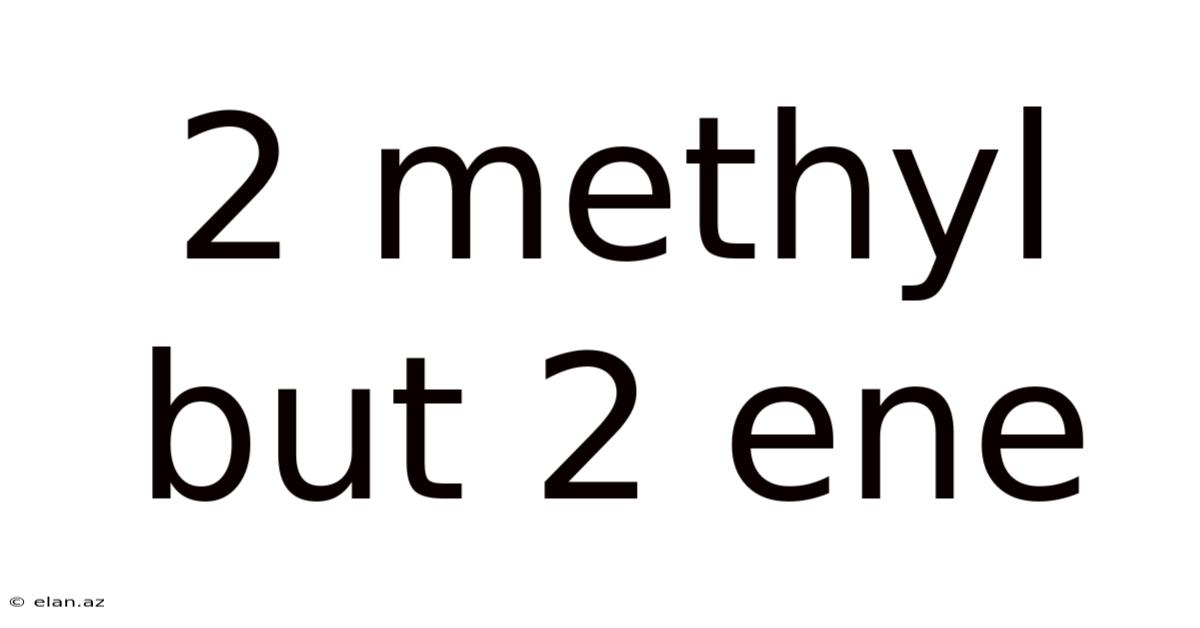
Table of Contents
Decoding 2-Methylbut-2-ene: Structure, Properties, Reactions, and Applications
2-Methylbut-2-ene, often abbreviated as 2M2B, is an unsaturated hydrocarbon belonging to the alkene family. Understanding its structure, properties, and reactivity is crucial for various applications in chemistry and related fields. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of 2-Methylbut-2-ene, providing a detailed overview suitable for students, researchers, and anyone interested in organic chemistry.
Introduction: Unveiling the Structure of 2-Methylbut-2-ene
2-Methylbut-2-ene is a branched alkene with the molecular formula C₅H₁₀. Its name systematically describes its structure:
- 2-Methyl: Indicates a methyl group (CH₃) attached to the second carbon atom.
- But: Refers to a four-carbon chain (butane).
- 2-ene: Specifies a double bond (alkene) located between the second and third carbon atoms.
This configuration results in a molecule with a highly substituted double bond, leading to unique chemical properties. The structural formula can be represented as:
CH₃
|
CH₃-C=CH-CH₃
This structural arrangement influences its reactivity and physical properties, distinguishing it from other isomers like 2-methylbut-1-ene and 3-methylbut-1-ene.
Physical Properties: A Closer Look at 2M2B
Several key physical properties define 2-Methylbut-2-ene:
- State: At room temperature and standard pressure, 2-Methylbut-2-ene exists as a colorless liquid.
- Boiling Point: It has a relatively low boiling point, approximately 38.5 °C, due to its relatively low molecular weight and the absence of strong intermolecular forces. This lower boiling point compared to its saturated counterpart, 2-methylbutane, reflects the weaker London Dispersion Forces present in alkenes due to their less polarizable electron clouds.
- Density: It possesses a lower density than water, making it less dense and immiscible with water.
- Solubility: Due to its nonpolar nature, 2-Methylbut-2-ene is insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents like hexane or ether. This is characteristic of hydrocarbons with predominantly nonpolar C-C and C-H bonds.
- Flammability: Like most hydrocarbons, 2-Methylbut-2-ene is highly flammable and should be handled with caution in the presence of ignition sources.
Chemical Reactivity: Exploring the Double Bond’s Role
The presence of the carbon-carbon double bond in 2-Methylbut-2-ene is the driving force behind its rich chemistry. This double bond, composed of a sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond, is relatively reactive compared to single bonds. The pi electrons are readily available for reactions, leading to a variety of transformations.
1. Addition Reactions: These are among the most characteristic reactions of alkenes. In addition reactions, the double bond breaks, and two new substituents add across the carbons previously involved in the double bond.
-
Halogenation: Reaction with halogens (e.g., chlorine, bromine) leads to the formation of vicinal dihalides. For example, reaction with bromine (Br₂) yields 2,3-dibromo-2-methylbutane. This reaction is often used to test for the presence of unsaturation.
-
Hydrohalogenation: Addition of hydrogen halides (e.g., HCl, HBr) follows Markovnikov's rule, where the hydrogen atom adds to the carbon atom with more hydrogen atoms already attached, while the halogen adds to the other carbon. Thus, the addition of HBr to 2-Methylbut-2-ene yields mainly 2-bromo-2-methylbutane.
-
Hydration: The addition of water (H₂O) in the presence of an acid catalyst (e.g., H₂SO₄) forms an alcohol. Following Markovnikov’s rule, the addition of water to 2-Methylbut-2-ene yields 2-methylbutan-2-ol.
-
Hydrogenation: The addition of hydrogen (H₂) in the presence of a metal catalyst (e.g., Pt, Pd, Ni) saturates the double bond, converting the alkene into an alkane. This reaction converts 2-Methylbut-2-ene into 2-methylbutane.
2. Oxidation Reactions: These reactions involve the addition of oxygen atoms or the removal of hydrogen atoms.
-
Ozonolysis: Reaction with ozone (O₃) followed by a reductive workup (e.g., Zn/H₂O) cleaves the double bond, producing carbonyl compounds. Ozonolysis of 2-Methylbut-2-ene yields acetone and acetaldehyde.
-
Combustion: Complete combustion of 2-Methylbut-2-ene in the presence of excess oxygen produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), releasing significant energy in the form of heat.
3. Polymerization: 2-Methylbut-2-ene can undergo polymerization, forming long chains of repeating units. This process requires suitable initiators and specific reaction conditions. The resulting polymer might find use in specialized applications, though it's not as common a polymer as those derived from ethylene or propylene.
Isomerism and Stereoisomers: Understanding the Variations
2-Methylbut-2-ene exhibits structural isomerism and can exist as stereoisomers.
-
Structural Isomers: Several structural isomers share the same molecular formula (C₅H₁₀) but differ in the arrangement of atoms. Examples include 2-methylbut-1-ene and 3-methylbut-1-ene. These isomers have different physical and chemical properties.
-
Stereoisomers: While 2-Methylbut-2-ene itself doesn't exhibit cis-trans isomerism (geometric isomerism) because the two substituents on each carbon of the double bond are the same, other alkenes with the formula C₅H₁₀ do. This highlights the importance of understanding isomeric variations within the broader alkene family.
Spectroscopic Characterization: Identifying 2M2B
Various spectroscopic techniques can be used to confirm the identity and purity of 2-Methylbut-2-ene:
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy: ¹H NMR and ¹³C NMR spectroscopy provide valuable information about the structure and the chemical environment of hydrogen and carbon atoms, respectively. The characteristic chemical shifts and splitting patterns can confirm the presence of the methyl groups and the double bond.
-
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy: IR spectroscopy reveals the presence of specific functional groups through characteristic absorption bands. The absence of an O-H stretch and the presence of C=C stretching vibrations (around 1650 cm⁻¹) are indicative of an alkene.
-
Mass Spectrometry (MS): Mass spectrometry can determine the molecular weight and fragmentation patterns of the molecule, providing further confirmation of its identity. The fragmentation pattern would reflect the structure's stability and bond strengths.
Applications of 2-Methylbut-2-ene: From Laboratory to Industry
While not as widely used as some other alkenes, 2-methylbut-2-ene finds applications in several areas:
-
Organic Synthesis: It serves as an important building block in organic synthesis, acting as a starting material for the preparation of various organic compounds. Its reactivity allows for the synthesis of more complex molecules with desired functionalities.
-
Polymer Chemistry: Although not a major component in common polymers, it can participate in polymerization reactions to create specialized polymers with specific properties depending on the polymerization conditions and initiators.
-
Research and Education: It is used extensively in educational settings to illustrate the properties and reactivity of alkenes. Its relatively simple structure makes it an ideal model for demonstrating concepts such as addition reactions, Markovnikov’s rule, and isomerism.
-
Industrial Applications (niche): Potential applications in specialized fields might exist, depending on the specific needs of particular industries or processes, though these applications are not as widely publicized or documented.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is 2-Methylbut-2-ene toxic?
A1: Like many organic compounds, 2-Methylbut-2-ene can be irritating to skin, eyes, and respiratory systems. Inhalation of high concentrations can lead to adverse health effects. Appropriate safety precautions, including wearing gloves, eye protection, and working in a well-ventilated area, are essential when handling this compound.
Q2: How is 2-Methylbut-2-ene produced?
A2: Several synthetic routes can lead to the production of 2-Methylbut-2-ene. One common method involves the dehydration of tertiary alcohols, such as 2-methylbutan-2-ol, in the presence of a strong acid catalyst like sulfuric acid.
Q3: What are the environmental concerns associated with 2-Methylbut-2-ene?
A3: As a volatile organic compound (VOC), it can contribute to air pollution and the formation of smog. Its flammability poses a fire hazard. Responsible handling and disposal practices are crucial to minimize environmental impact.
Q4: What are the differences between 2-Methylbut-2-ene and other isomers?
A4: The key difference lies in the position of the double bond and the resulting differences in reactivity. The highly substituted double bond in 2-methylbut-2-ene influences its reaction rates and the regioselectivity of addition reactions.
Conclusion: A Versatile Alkene with Diverse Potential
2-Methylbut-2-ene, though perhaps not as widely known as some other hydrocarbons, offers a fascinating case study in organic chemistry. Its unique structure, influenced by the branched alkyl chain and the highly substituted double bond, leads to distinct physical and chemical properties. Its relatively simple structure makes it an excellent model compound for understanding fundamental organic reactions and concepts. While its applications might not be as prevalent as some other alkenes, its role in organic synthesis, polymerization research, and education remains significant. Future research might uncover further applications, expanding the scope of its utilization in various fields. Safe handling and environmentally conscious use are critical for both laboratory and industrial applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Carbon Dioxide Dot And Cross
Sep 18, 2025
-
A Perimeter Of A Rectangle
Sep 18, 2025
-
Verbs To Describe A River
Sep 18, 2025
-
How To Become A Shareholder
Sep 18, 2025
-
Vegetables That Start With K
Sep 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 2 Methyl But 2 Ene . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.