76 Degrees F To C
elan
Sep 15, 2025 · 6 min read
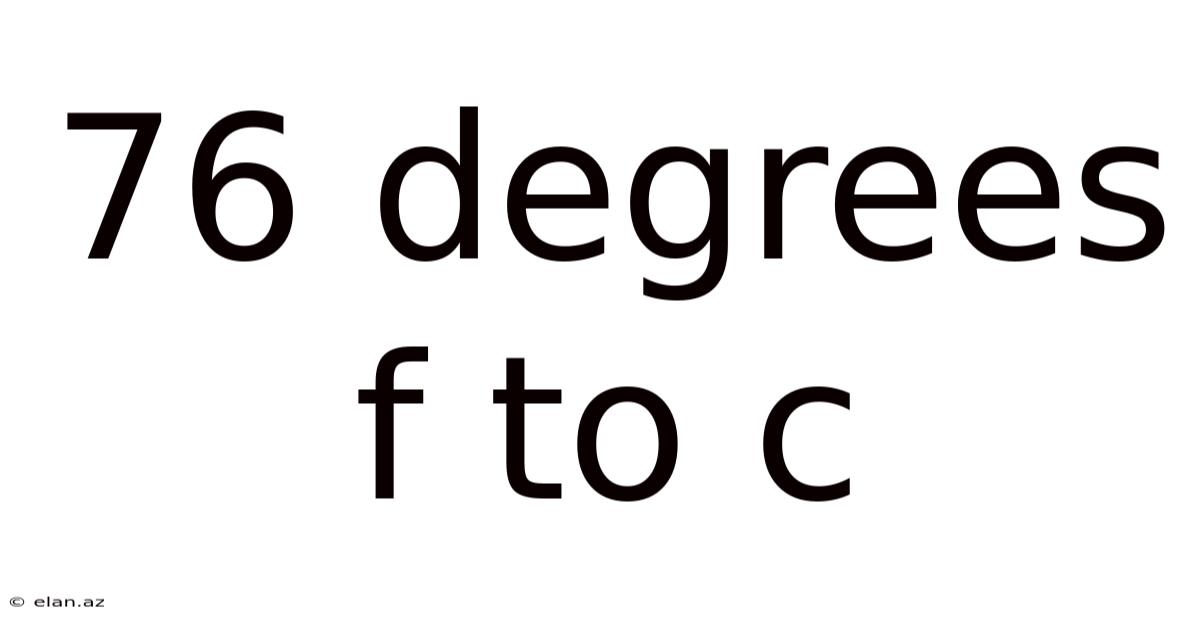
Table of Contents
Converting 76 Degrees Fahrenheit to Celsius: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered how to convert temperatures between Fahrenheit and Celsius? This seemingly simple task is essential in many fields, from cooking and weather forecasting to scientific research and engineering. This article provides a comprehensive guide to converting 76 degrees Fahrenheit (°F) to Celsius (°C), explaining the process, the underlying formula, and offering helpful tips and examples for future conversions. We'll also delve into the history of these temperature scales and explore some common applications of temperature conversions.
Understanding Fahrenheit and Celsius
Before jumping into the conversion, let's briefly understand the two scales. The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, uses the freezing point of water as 32°F and the boiling point as 212°F. The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, was developed by Anders Celsius and uses 0°C for the freezing point of water and 100°C for its boiling point. The Celsius scale is the preferred scale in most of the world and is used in scientific contexts.
The Conversion Formula: From Fahrenheit to Celsius
The core of the conversion lies in a simple formula:
°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9
This formula takes the Fahrenheit temperature, subtracts 32 (to adjust for the difference in freezing points), and then multiplies the result by 5/9 (to account for the different scale increments).
Converting 76°F to Celsius: A Step-by-Step Guide
Now, let's apply this formula to convert 76°F to Celsius:
-
Start with the Fahrenheit temperature: We have 76°F.
-
Subtract 32: 76°F - 32°F = 44°F
-
Multiply by 5/9: 44°F × 5/9 = 24.44°C (approximately)
Therefore, 76 degrees Fahrenheit is equal to approximately 24.44 degrees Celsius.
Practical Applications of Temperature Conversions
Understanding temperature conversions is crucial in various everyday situations and professional fields. Here are a few examples:
-
Cooking: Many recipes, especially those originating from countries using the Celsius scale, provide temperatures in Celsius. Knowing how to convert ensures accurate cooking and baking results. For instance, a recipe calling for 180°C would need to be converted to Fahrenheit for use in an oven with a Fahrenheit display.
-
Weather Forecasting: Weather reports often provide temperatures in both Fahrenheit and Celsius, catering to a diverse audience. The ability to convert allows you to easily understand weather reports regardless of the scale used.
-
Scientific Research: Across scientific disciplines, the Celsius scale is the standard. Researchers frequently need to convert temperatures obtained from instruments calibrated in Fahrenheit to Celsius for data analysis and reporting.
-
Engineering: In many engineering applications, especially those dealing with materials science and thermodynamics, the ability to seamlessly switch between Fahrenheit and Celsius is essential for accurate calculations and design.
-
International Travel: When traveling internationally, understanding temperature conversions is critical to packing appropriate clothing and anticipating the weather conditions.
Beyond the Formula: Understanding the Rationale
The formula (°C = (°F - 32) × 5/9) isn't arbitrary. It's derived from the fundamental differences between the two scales:
-
Different Zero Points: The Fahrenheit scale has a zero point that doesn't align with the freezing point of water. Subtracting 32 compensates for this difference.
-
Different Scale Increments: The Fahrenheit scale has a smaller increment between degrees compared to the Celsius scale. Multiplying by 5/9 adjusts for this difference in the size of the degrees.
This formula ensures a consistent and accurate conversion between the two scales.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While the conversion formula is straightforward, some common mistakes can lead to incorrect results:
-
Order of Operations: Always perform the subtraction before the multiplication. Failing to follow the order of operations will result in an incorrect answer.
-
Incorrect Fraction: Ensure you use the correct fraction (5/9), not 9/5. Using the wrong fraction will significantly alter the result.
-
Rounding Errors: Be mindful of rounding errors. While 24.44°C is a perfectly acceptable approximation, in some contexts, more precise calculations might be necessary, requiring more significant figures in the calculation.
Advanced Concepts: Kelvin Scale
While Fahrenheit and Celsius are commonly used, the Kelvin scale is the absolute temperature scale. Zero Kelvin (0 K) represents absolute zero, the theoretical lowest possible temperature. The Kelvin scale is crucial in scientific research and engineering, particularly in areas dealing with thermodynamics. The relationship between Celsius and Kelvin is:
K = °C + 273.15
This means that to convert from Celsius to Kelvin, you simply add 273.15. Conversely, to convert from Kelvin to Celsius, you subtract 273.15.
A Deeper Dive into the History of Temperature Scales
The development of temperature scales reflects the evolution of scientific understanding. Fahrenheit's scale, while now less prevalent, reflects the limitations of early thermometry. His scale used a mixture of ice, water, and ammonium chloride to define his zero point, leading to an arbitrary zero. Celsius' scale, with its clear and consistent reference points (freezing and boiling points of water), proved to be more practical and scientifically sound, making it the preferred standard for scientific purposes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Can I convert Celsius to Fahrenheit?
A1: Absolutely! The reverse conversion formula is: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Q2: What are some online calculators for temperature conversions?
A2: Many websites and apps offer temperature conversion calculators. However, understanding the underlying formula is crucial for developing a deeper understanding of temperature scales.
Q3: Why is the Celsius scale preferred in science?
A3: The Celsius scale's clear reference points (0°C and 100°C) and its direct relationship with the Kelvin scale make it more suitable for scientific calculations and experiments.
Q4: Is it possible to have negative temperatures in Celsius?
A4: Yes, temperatures below the freezing point of water (0°C) are represented as negative values in the Celsius scale.
Q5: What is the significance of absolute zero?
A5: Absolute zero (0 K) represents the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. It's a fundamental concept in thermodynamics and is unattainable in practice.
Conclusion
Converting 76°F to Celsius, while seemingly simple, opens up a broader understanding of temperature scales and their applications. This article has not only provided the conversion but also explained the rationale behind the formula, explored practical applications, and offered insights into the history and significance of different temperature scales. Mastering temperature conversions is a valuable skill with wide-ranging applications in various fields, ensuring accuracy and ease of communication across different systems of measurement. Remember to always double-check your calculations and consider the context of your conversion to avoid any errors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Difference Between Magnification And Resolution
Sep 15, 2025
-
Biology Cells Tissues And Organs
Sep 15, 2025
-
Device For Measuring Electrical Resistance
Sep 15, 2025
-
Advent Of The Three Calamities
Sep 15, 2025
-
How To Work Out Tangent
Sep 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 76 Degrees F To C . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.